Why Your Website Is Not Indexed on Google and How to Fix It
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is Google Indexing?
- Why Fixing Google Indexing Issues Is Important
- What Are the Reasons a Website Is Not Indexed on Google Search Results?
- How Do Indexing Issues Affect a Website’s Presence on Google?
- How to Check If Your Website Is Not Indexed on Google
- How to Fix Website Google Indexing Issue
- Conclusion
Introduction
Is your Website site not indexed on Google? You’re not alone. Many website owners face this frustrating issue. Your website looks great, but it doesn’t appear on Google. It’s a serious concern, especially if you’re relying on organic traffic. You can read this article to learn why this occurs and what you can do about it.
Indexing is the process Google uses to read and store your site’s content. Your pages won’t appear in search results if they aren’t indexed. In simple terms, if your site isn’t indexed, Google can’t find or display it.
This guide covers what Google indexing means, the common Website Indexed issue, and how to fix it. We’ve broken it down into easy sections to help you follow along.
Let’s begin by understanding what indexing means and why it matters.
What Is Google Indexing?
Google indexing is how website data is stored and organized in Google’s search index, which holds billions of web pages. It’s the primary source from which Google retrieves results for user queries. Without indexing, web pages do not appear in Google’s search results.
Indexing begins after Googlebot, the web crawler, discovers a web page. It reads the content, including text, titles, meta tags, links, and structured data. Once crawled, Google processes this information and stores it in its index. This makes the content retrievable when users search for related terms.
If a Website site not indexed, it will not appear in organic search. This is a common Website indexing problem faced by many site owners. In such cases, Google not indexing Website pages may indicate a deeper Website crawl indexing issue. Often, these issues are connected to incorrect settings, blocked resources, or poor technical SEO.
Every page that appears in Google search must be indexed first. If your Website not indexing, then no matter how well-optimized your content is, it won’t rank. This is why resolving a Website Indexed issue is critical for visibility and performance.
When users say their Website not showing in Google, it usually means the content hasn’t been crawled or indexed properly. This Website visibility issue may affect individual pages or entire websites. Even if the site is live, the site not appearing Google means it is excluded from Google’s index.
To better understand why Website not indexed on Google result, site owners must check their Search Console coverage reports. This tool can highlight crawl errors, page exclusions, or Website SEO indexing issues that prevent content from being stored in the index.
Technically, indexing is step two in the search process:
- Crawling: Googlebot discovers content across the web.
- Indexing: Google processes and stores valuable pages.
- Ranking: Algorithms evaluate indexed pages and show the most relevant ones.
When indexing is successful, a web page becomes part of the structured data system Google uses to answer search queries. If the indexing step fails, the content remains invisible to users searching online.
Why Fixing Google Indexing Issues Is Important
- Improves Website Visibility in Google Search
If your pages are not indexed, they won’t appear on Google. Fixing indexing ensures your content shows in search results. Visibility is the first step to gaining traffic, ranking, and growing your audience through organic search. - Drives More Organic Traffic to Your Website
Indexing issues block your content from reaching search users. Fixing them lets Google display your site for relevant keywords. More indexed pages mean more chances to drive targeted organic traffic from search engines to your site. - Helps Your Content Appear for Relevant Keywords
When Google indexes your site, it links it with keywords. Unindexed content won’t rank for any keyword. Fixing these issues helps search engines match your content with user queries and show it in results. - Boosts Your SEO Performance Across the Website
Search Engine Optimization depends on proper indexing of every page. Broken indexing impacts your entire SEO strategy. Fixing it ensures your on-page, technical, and content SEO efforts get the visibility they deserve. - Ensures Googlebot Understands and Stores Your Pages
Googlebot must read and understand your site to index it. If there’s an error, it may skip your content. Fixing issues ensures the crawler can access, scan, and store your pages correctly. - Prevents Loss of Leads, Sales, and Conversions
If your landing pages aren’t indexed, users can’t find them. This leads to traffic loss and missed sales opportunities. Fixing indexing problems ensures important pages are reachable and converting visitors into customers. - Keeps You Ahead of SEO Competitors in Rankings
Unindexed pages fall behind in search engine results. Competitors with fully indexed sites outrank you easily. Fixing issues gives you a fair chance to compete and perform better on search engines. - Allows Full Use of Google Search Console Features
Without proper indexing, your Search Console data is incomplete. Fixing issues helps you track page performance, impressions, and clicks. You get more accurate insights to improve your SEO and content strategy. - Strengthens Your Website’s Technical Health
Indexing issues often signal deeper technical problems. Fixing them improves crawlability, site structure, and page performance. A clean index ensures Google sees your site as well-maintained and high quality. - Builds Trust with Search Engines and Users
A well-indexed site sends trust signals to Google. It shows your site is functional, useful, and reliable. Fixing issues builds long-term trust with both search engines and potential visitors.
What Are the Reasons a Website Is Not Indexed on Google Search Results?
- Duplicate Content
Duplicate pages confuse Google and harm indexing. If the same content appears in multiple places, it may be skipped. This can cause a Website Indexed issue. Ensure your site offers unique value and avoids repeating text across URLs. - Your Website Is New
New websites take time to be crawled and indexed. If your Website site not indexed yet, it’s likely not discovered. Submit your sitemap in Search Console and request indexing manually to speed up the process. - Blocked by Robots.txt
A restrictive robots.txt file can block Googlebot from crawling your site. This results in Google not indexing Website content. Always allow access to important folders and test the file using the Search Console robots tester. - Crawl Budget Issues
Google allocates limited crawl resources to every site. If you exceed this, pages may be skipped. Large or poorly structured sites often suffer crawl delays, leading to Website crawl indexing issues. Optimize crawl settings and fix duplicate paths. - Google Index Problems
Sometimes, indexing issues happen on Google’s side. A glitch may delay indexing even if your site is ready. If your Website not showing in Google, check the Index Coverage report in Search Console for updates. - Poor Content Quality
Low-quality or thin content may be excluded from indexing. Google looks for useful, trustworthy content. A Website SEO indexing issue can occur when pages lack depth or value. Add better information and structure to your content. - Lack of Backlinks
If your site has no links pointing to it, Google might ignore it. Backlinks help discover and prioritize pages. This can lead to a site not appearing Google situation. Build quality external links from trusted sources. - Weak Internal Linking Structure
Internal links help Googlebot discover deeper content. If links are missing, important pages may not be crawled. This contributes to a Website visibility issue. Always link related pages and create a strong internal structure. - Improper Redirects
Faulty redirects confuse crawlers and block indexing. If redirects lead to broken or irrelevant pages, indexing will fail. Redirect chains and loops can also result in a Website indexing problem. Use proper 301 redirects and avoid redirect overload. - Crawl Errors on Site
Crawl errors like 404, 500, or DNS failures prevent indexing. Check the Crawl Stats and Index Coverage in Search Console. A Website not indexing issue may be triggered by frequent server or DNS errors. - Blocked by Noindex Tag or Header
“Noindex” directives in meta tags or HTTP headers prevent indexing. If a page has this tag, it won’t show up in search. This directly causes a Website site not indexed problem. Remove noindex for content meant to rank. - URL Marked “Noindex” in Plugins
SEO plugins often let users set pages as noindex. If misused, pages are hidden from search. This is a common Website SEO indexing issue. Always review your plugin settings and mark only necessary pages as noindex. - Slow Website Speed
A slow-loading site reduces crawl efficiency. Googlebot may abandon crawling. This leads to a Website crawl indexing issue. Optimize images, use caching, and test performance regularly to improve speed and indexing frequency. - Searching via Google Site Operator Only
Sometimes pages are indexed but don’t rank or appear in search. Use site:yourdomain.com to confirm if your content is in the index. If not, your Website not showing in Google might be a discovery or ranking issue. - Incorrect Canonical Tags
Wrong canonical tags tell Google which version to index. If set incorrectly, preferred pages may be ignored. This leads to a Website Indexed issue. Review canonical URLs to ensure they point to the correct version of the page. - Indexed Page Without Content
Sometimes Google indexes empty or template pages. These bring no value and reduce site quality. A Website indexing problem may occur if key content is missing from indexed pages. Always publish complete, content-rich pages. - Search Intent Mismatch
Pages not aligned with user intent might not be indexed. If content doesn’t answer queries clearly, Google may skip it. A Website visibility issue can stem from unclear targeting. Ensure each page serves a clear search purpose. - SEO Not Properly Done
Poor SEO setup hurts indexing. Missing meta tags, improper headers, or broken structure confuse crawlers. This often results in Website not indexing properly. Set up your SEO plugin correctly and follow on-page optimization best practices. - Server Errors Prevent Crawling
If your server returns 5xx errors or downtime, Googlebot can’t crawl. This causes your Website site not indexed despite good content. Use uptime monitors and check logs to prevent and resolve these technical issues. - Minimal High-Quality Content on Site
If your website has very little useful information, indexing may be limited. Google favors content-rich pages. Lack of content leads to a Website SEO indexing issue. Add detailed, well-formatted content to improve index chances. - Broken Links on Pages
Pages with many broken links reduce crawl success. Google may stop indexing if navigation fails. Fixing broken internal or external links can solve your Website not showing in Google issue and improve overall crawl health. - Empty or Generic Content Pages
Pages with filler or placeholder content will likely be skipped. Google doesn’t index pages with no value. These pages cause a Website Indexed issue that lowers site quality signals. - Too Many Duplicate Pages
Excessively similar pages confuse Googlebot and reduce indexing chances. Multiple similar pages can trigger a Website indexing problem. Consolidate or redirect duplicate URLs to a single, authoritative version to avoid redundancy. - Manual Action Penalty by Google
If Google detects violations of its policies, it may apply a penalty. A manual action can block indexing and de-rank existing content. Check Search Console’s “Manual Actions” report and resolve all flagged issues immediately. - Indexing Disabled in Website Settings
A common reason for a Website site not indexed is a setting issue. If the “Discourage search engines” box is checked, Googlebot won’t crawl. This simple checkbox can block indexing. Always check Website Reading Settings and ensure indexing is allowed for your site.
How Do Indexing Issues Affect a Website’s Presence on Google?
- Website Doesn’t Appear in Google Search Results
If pages aren’t indexed, they won’t show in search results. Users searching your brand or content won’t find your site. This reduces visibility and limits potential traffic. Fixing indexing ensures your pages are searchable and available to your audience on Google. - Drop in Organic Traffic and Visitor Count
When pages aren’t indexed, they won’t generate organic clicks. Even high-quality content goes unseen. This leads to a sharp drop in traffic. Without proper indexing, your SEO efforts won’t deliver the expected results or audience reach through search engines. - Content Fails to Rank for Relevant Keywords
Unindexed content cannot compete in keyword rankings. Google skips it during ranking evaluation. Even optimized pages won’t rank. This impacts your ability to attract targeted users and generate engagement through important search terms related to your business. - Reduced Site Authority in Google’s View
Indexing issues send weak trust signals to Google. A site missing pages from the index looks incomplete. This can lower domain authority. Google prefers fully indexed, healthy websites that are regularly updated and structured for both users and crawlers. - SEO Efforts Become Ineffective
On-page and technical SEO won’t matter if pages are unindexed. Even great titles, meta tags, and schema go to waste. Your Website SEO indexing issue can block progress. Fixing indexing allows your SEO to deliver measurable results. - Important Pages May Be Missed by Users
If product, service, or contact pages aren’t indexed, users can’t reach them. This leads to poor user experience and lost conversions. Ensuring complete indexing keeps critical pages available and searchable for visitors coming from Google. - Search Console Reports Incomplete Performance Data
Google Search Console shows data only for indexed pages. Unindexed content is excluded from impressions and click stats. This gives you a partial view of website performance. Fixing indexing allows accurate data tracking and helps guide SEO decisions. - New Content Doesn’t Get Discovered
Fresh blog posts or updated pages won’t appear if not indexed. This limits your ability to stay current in search results. Timely indexing is crucial to stay visible with trends, updates, or breaking information that users are actively searching. - Lower Engagement and Conversions from Organic Visitors
Without indexing, you lose opportunities to reach new customers. Content won’t appear, so fewer users land on your site. This leads to lower engagement, fewer leads, and reduced conversions—all because your content isn’t showing up in Google Search. - Missed Opportunities for Featured Snippets and Rich Results
Indexed content is eligible for rich results and featured snippets. If your page isn’t indexed, it won’t qualify. These features drive more clicks and visibility. Fixing indexing issues increases your chance to appear in enhanced listings above other results.
How to Check If Your Website Is Not Indexed on Google
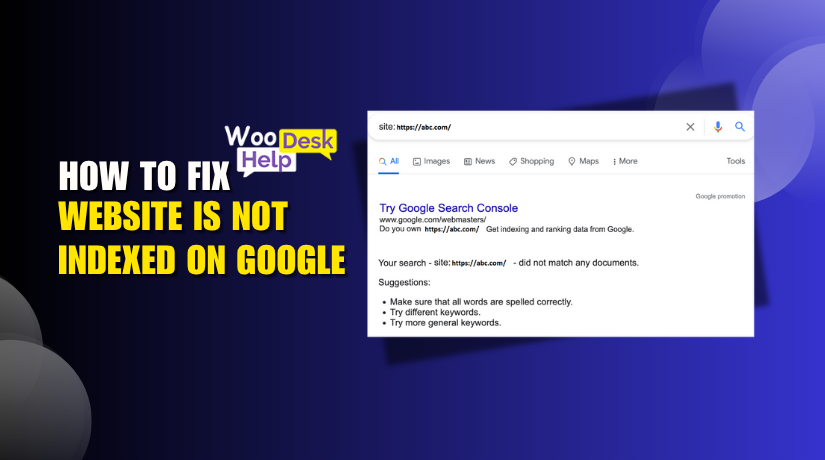
- Use the site: search operator on Google
The simplest way to check if your site is indexed is by using the site: search operator. Go to Google and type site:yourdomain.com. If your pages appear in the results, they are indexed. If nothing shows, your site is likely not indexed. This method works well for checking a few URLs or an entire domain quickly, but it’s not always 100% accurate for large websites. - Use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console
Log in to Google Search Console and use the URL Inspection tool. Enter a complete page URL and press enter. Google will tell you if the page is indexed or not. It also provides details like when the page was last crawled, how it was discovered, and if there are any indexing errors. This is one of the most accurate ways to check individual page indexing status. - Check the Index Coverage report in Search Console
In the Search Console dashboard, navigate to the “Indexing” section and click on “Pages.” This report shows which pages are indexed and which are not. It also lists the reasons why some pages may be excluded. If you see many excluded or error pages, your site may have broader indexing issues that need fixing. - Use a bulk index checker tool
If you have many URLs to check, using a bulk index checker tool can save time. Tools like DupliChecker or SEO suites like Ahrefs and Semrush allow you to paste multiple URLs and get the indexing status for each one. This method is ideal for larger sites with hundreds or thousands of pages. - Check the Google Cache for specific pages
Type cache:yourpageurl.com into Google’s search bar. If a cached version of the page appears, that means Google has indexed it at some point. You can also see the last date Googlebot visited. If there’s no cache available, the page is likely not indexed yet. - Apply custom date filters in Google Search
Search for your page’s title or keyword in Google, then apply a custom date filter from search tools. Set the date back a few months. If your page appears with a visible date, it was indexed. This method helps estimate when the page was first seen by Google. - Run a live test with Search Console
Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool includes a “Live Test” feature. This checks if your page can be accessed and crawled in real time. While it doesn’t guarantee the page is indexed, it confirms whether the page is working and visible to Googlebot right now. - Submit and monitor your sitemap
Ensure your XML sitemap is submitted in Google Search Console under the “Sitemaps” section. After submission, check the sitemap indexing status in the Index Coverage report. It shows how many URLs from your sitemap are indexed, excluded, or have errors. This is very useful for ongoing tracking of large websites. - Understand the limits of the site: search method
The site: operator is a quick check but has limitations. It often doesn’t return complete results, especially for websites with many pages. You might miss some indexed URLs this way. That’s why Search Console is a better tool for full visibility. Use both methods together for best results. - Use SEO software for regular indexing audits
Tools like Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, or Rank Math for Website can crawl your website and identify which URLs are indexed or not. They also show canonical errors, redirect chains, noindex tags, and broken links. These tools are essential for webmasters managing large websites or eCommerce platforms.
How to Fix Website Google Indexing Issue
- Check If Your Website Is Indexed
Start by checking if your website is already indexed by Google. Go to Google and type woohelpdesk.com. If no pages appear, your website has not been indexed yet. This confirms the issue. You can also log in to Google Search Console and check under the “Pages” section. This is the easiest way to identify indexing problems early.
- Set Up Google Search Console
To manage and fix indexing issues, connect your website to Google Search Console. Visit search.google.com/search-console, add your website, and verify ownership. Use DNS records, HTML files, or meta tags to verify. Once done, you can track crawl status, indexing errors, and fix problems directly.
- Submit Your Sitemap to Google
An XML sitemap helps Google understand the structure of your site. Create a sitemap using an SEO plugin or sitemap generator. In Google Search Console, go to the “Sitemaps” section and enter your sitemap URL (e.g., yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml). This allows Google to find and crawl your important pages faster.
- Use the URL Inspection Tool
If a specific page is missing from Google, use the URL Inspection tool. Enter the full URL into the tool inside Search Console. It will show whether the page is indexed or not. If not, click “Request Indexing” to ask Google to index the page manually.
- Remove ‘Noindex’ Tags From Important Pages
Check your HTML or SEO plugin settings for any noindex tags. These tags tell Google not to index the page. If applied accidentally, your pages won’t appear in search. Remove the tag from any page that should be indexed, then re-submit the URL in Search Console.
- Check Your Robots.txt File
A misconfigured robots.txt file may block Google from crawling pages. Open yourdomain.com/robots.txt and look for lines like Disallow: /. If important pages are blocked, edit the file and remove those rules. Google must be able to crawl pages before it can index them.
- Fix Duplicate and Low-Quality Content
Google avoids indexing pages with thin or duplicate content. Go through affected pages and improve the content. Add value with helpful information, images, or FAQs. Make sure the content is original and solves user problems. Well-written pages are more likely to be indexed and ranked.
- Link Orphan Pages Internally
Orphan pages are not linked from anywhere on your website. Googlebot might not discover them. Add internal links from blogs, menus, or homepage to those pages. This improves visibility and helps Google crawl and index them easily.
- Resolve Redirect and Broken Link Issues
Redirect chains and broken links create crawl problems. Use tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs to identify 404 errors and bad redirects. Fix all broken URLs and use 301 redirects where needed. A clean URL structure makes indexing easier for search engines.
- Improve Site Speed and Mobile Usability
Slow websites or poorly optimized mobile designs can limit crawling. Use PageSpeed Insights to test your site’s performance. Compress images, enable caching, and remove unnecessary scripts. Make sure your website works well on mobile devices too.
- Build Quality Backlinks to Key Pages
Pages with no backlinks may not get indexed quickly. Share your content on social media, forums, or directories. Reach out for guest posting or link building. Quality backlinks help Google discover and index your site faster.
- Validate Your Fixes in Google Search Console
After fixing errors, go back to the “Pages” report. Click the issue (like “Not Found” or “Excluded by Noindex”) and then click “Validate Fix.” Google will re-crawl and check your updates. You’ll receive a message once validation is complete.
Conclusion
If your website isn’t indexed on Google, your content won’t be found. That means no search visibility, no organic traffic, and no growth. Whether you run a Website site or any other platform, indexing is the first step to success online.
From misconfigured settings to noindex tags, crawl errors, or poor internal linking—there are many reasons your pages might not appear on search results. But the good news is, most indexing issues are completely fixable. With the right tools like Google Search Console and a clear step-by-step process, you can get your site back into Google’s index.
For site owners dealing with Website not indexing, site not appearing in Google, or crawl indexing issues, resolving this quickly is essential. Make sure your technical SEO is clean, content is strong, and all crawl paths are open.
If you’re still unsure how to fix it or need expert support, visit www.woohelpdesk.com — your trusted partner for Website and WooCommerce support.
📞 Need help now? Call us at +1 888 602 0119 (US & Canada)
Don’t wait. Fix your indexing issues today and bring your website back to life in Google Search.




